The Inflation Reduction Act created a first-of-its-kind, national-scale program: the Greenhouse Gas Reduction Fund—to mobilize financing and private capital to address the climate crisis in the United States.
As we all have celebrated this historic event the idea is now, we must face this imperative by looking toward the talent needs for successful execution.
This transition goes beyond environmental considerations; it covers economic, social, and developmental dimensions, making it a critical priority for community development finance (CDF). As the sector grapples with the challenges and opportunities presented by the historic announcement to address climate transition, the demand for specialized talent is now the focus.
Here’s why harnessing best-in-class climate transition talent is essential for the CDF community:
The Climate Imperative
Climate change poses existential threats to communities worldwide, exacerbating vulnerabilities and inequalities. Community development finance has a pivotal role in financing initiatives that promote resilience, mitigation, and adaptation. From renewable energy projects to green infrastructure and sustainable housing, the sector is now front and center of driving climate action at the local level.
The Role of Talent
Talent is the lifeblood of any industry, and the CDF sector is no exception. However, in the context of climate transition, the demand for specialized skills and expertise is particularly acute. Here’s why:
Climate Finance Expertise: Professionals with a deep understanding of climate finance mechanisms, such as carbon markets, green bonds, and climate risk assessment, are indispensable. They can navigate the complexities of financing sustainable projects while ensuring alignment with climate goals.
Environmental Science and Engineering: Climate transition requires technical know-how in areas such as renewable energy, energy efficiency, and ecological restoration. Experts in environmental science and engineering play a critical role in designing and implementing climate-resilient infrastructure projects.
Policy and Advocacy: Climate policies and regulations shape the landscape for community development finance. Professionals with expertise in policy analysis, advocacy, and stakeholder engagement can influence decision-making processes, advocate for supportive policies, and drive systemic change.
Data Analytics and Technology: Data-driven insights are essential for assessing climate risks, measuring impacts, and optimizing investment strategies. Professionals skilled in data analytics, GIS (Geographic Information Systems), and technology can harness data to inform decision-making and enhance project outcomes.
Meeting the Talent Gap
Addressing the talent gap in climate transition requires a multifaceted approach:
Education and Training: Institutions now offer specialized programs and courses in climate finance, sustainable development, and related fields to equip future professionals with the necessary skills and knowledge.
Cross-Sector Collaboration: Collaboration between academia, government, NGOs, and the private sector can facilitate knowledge sharing, capacity building, and the development of interdisciplinary solutions to complex climate challenges.
Diversity and Inclusion: Embracing diversity and inclusion in the workforce enhances innovation, creativity, and effectiveness. Efforts to recruit, retain, and promote diverse talent must be prioritized to ensure equitable representation and perspectives in decision-making processes.
Professional Development: Continuous learning and professional development opportunities, such as workshops, seminars, and certifications, enable professionals to stay abreast of emerging trends, best practices, and evolving regulatory frameworks in climate finance.
As the CDF community navigates the Inflation Reduction Act/GGRF program promoting the transition to a sustainable future, harnessing climate transition talent is not just a necessity—it’s an opportunity for innovation, resilience, and positive impact. By investing in education, fostering collaboration, promoting diversity, and supporting professional development, the sector can build a skilled workforce capable of driving meaningful change and building climate-resilient communities for generations to come.
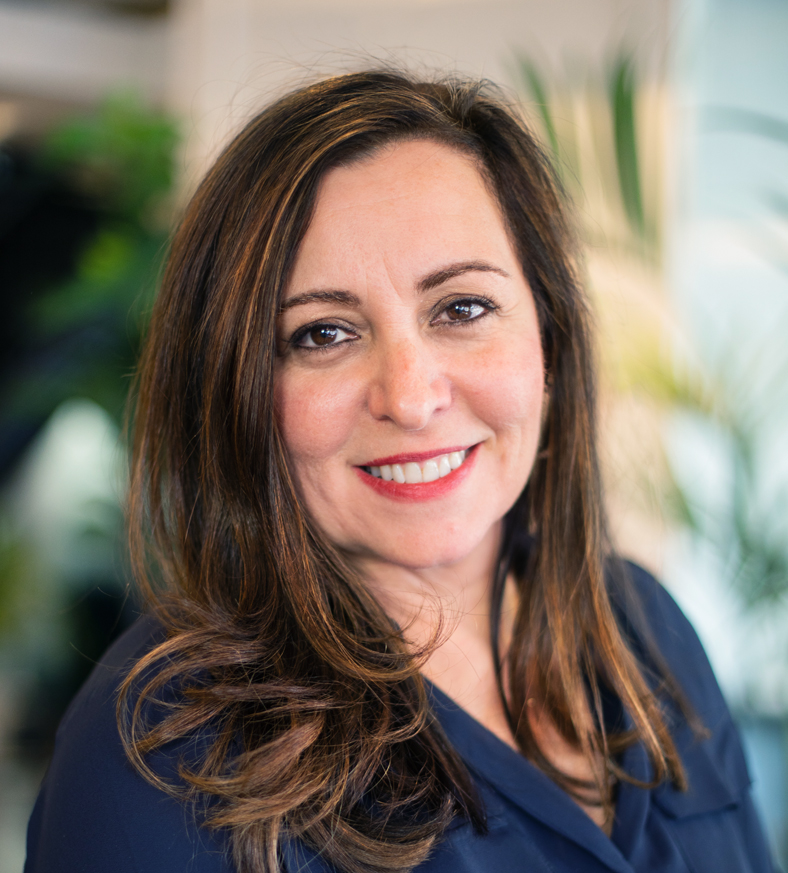
For further information on this topic or to discuss talent within your organization please contact Gloria, Executive Director & Head of Sustainable Finance & Impact Investing – Americas, at gloria.mirrione@acre.com.
%20(15).png)